Intelligent Condition Monitoring Framework For Solenoid Pumps
 Despite their relatively smaller sizes, solenoid pumps are capable of generating high-pressures for most low-scale and large-scale industrial applications respectively. They operate by a magnetization of the solenoids (electric coils) when electrical current passes through the coil which then causes the electromagnetic core to move against a spring to slide a diaphragm into the discharge position, thereby pumping fluid.
Despite their relatively smaller sizes, solenoid pumps are capable of generating high-pressures for most low-scale and large-scale industrial applications respectively. They operate by a magnetization of the solenoids (electric coils) when electrical current passes through the coil which then causes the electromagnetic core to move against a spring to slide a diaphragm into the discharge position, thereby pumping fluid.
The major objectives of the project are:
- To conduct FMECA on VSC63A5 solenoid pumps.
- To design and simulate test beds for multi-failure mode and run-to-failure tests for fault diagnosis and prognosis respectively for the pumps.
- To extract vibrational, thermal, and pressure responses (data) for developing AI-based models for intelligent condition monitoring and decision-making.
- To evaluate the performance of the developed models on real industrial equipment for validation.
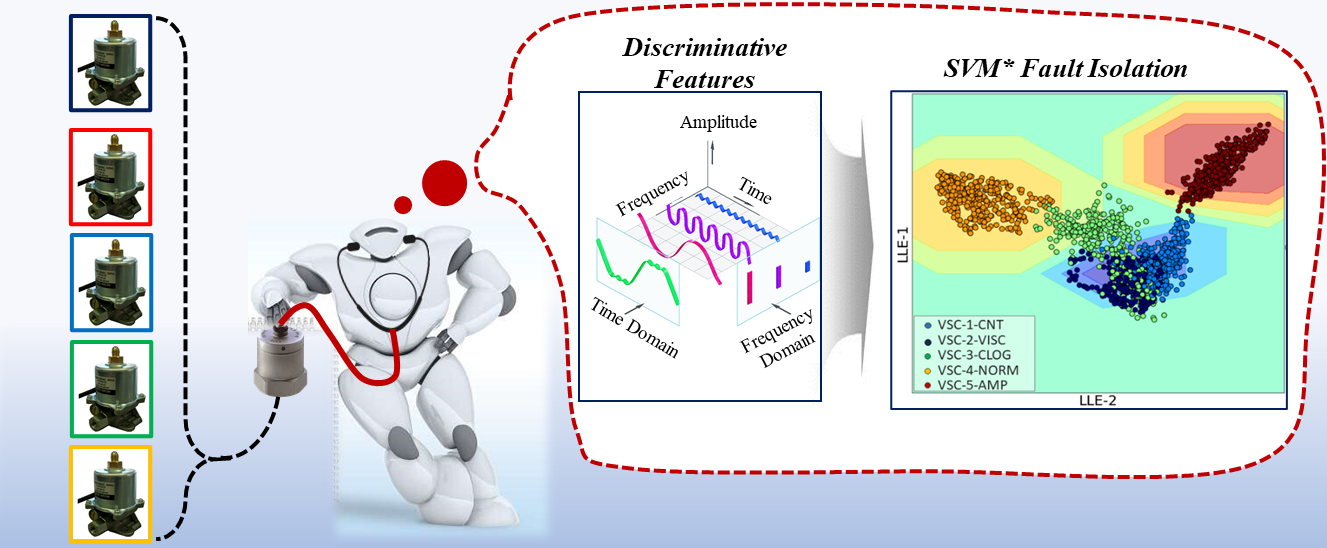
At the time of the project, no existing condition monitoring framework existed for solenoid pumps. This research gap motivated my proposal of a vibration monitoring approach that is fundamentally dependent on the exploitation of mel-frequency cepstral coefficients from the vibration signals. The VSC series solenoid pumps manufactured by Korea Control Limited pump fluids (light fuels like kerosene, and diesel) at a maximum discharge flowrate of about 17 Litres/hour; however, the VSC63 model when connected to the specified nozzle (1.0-1.5GPH), pumps fluid (diesel) at a discharge pressure— 0.5-1.0 MPa under normal conditions (an AC power supply of (220V, 60Hz) and room temperature). 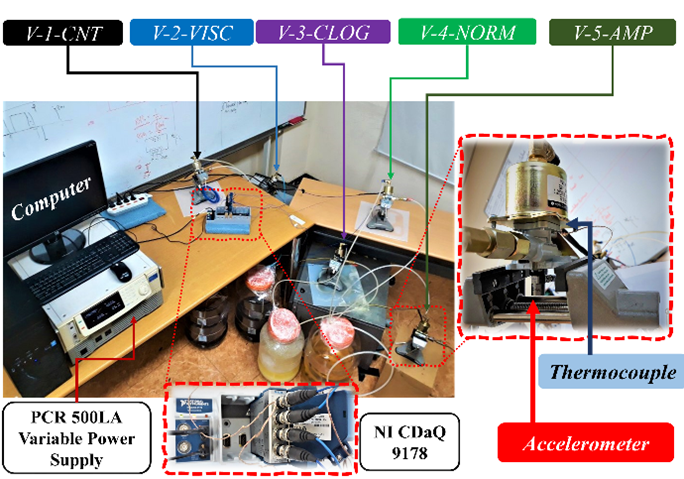
Grants
- Grand Information Technology Research support (IITP-2020-2020-0-01612) provided by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT) South Korea (2020 -2021)
- Korean National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (No. NRF-2019R1I1A3A01063935) provided by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT) South Korea (2019).
- Agency for Defense Development grant (UD180018AD) provided by the RAM Specialized Laboratory, South Korea (2019).
Selected Journal Publications from the project
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “A Cost-Efficient MFCC-Based Fault Detection and Isolation Technology for Electromagnetic Pumps,” in Electronics, vol. 10, no. 4:439, 2021
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “MFCC-LLE-SVM*: A Robust Fault Diagnostics Tool for Solenoid Pumps,” presented at PHM Korea 2020, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 188, July 21-23, 2020.
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “A Multi-Domain Diagnostics Approach for Solenoid Pumps Based on Discriminative Features,” in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 175020-175034, 2020
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “An Automated Sensor Fusion Approach for The RUL Prediction of Electromagnetic Pumps,” in IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 38920-38933, 2021.
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “D-dCNN: A Novel Hybrid Deep Learning-Based Tool for Vibration-Based Diagnostics,” in Electronics, 14, 5286, 2021.
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “A DNN-Based Fault Detection & Isolation Technology for Solenoid Pumps,” presented at The 2021 Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers Spring Conference, PS8-5, June 24-26, 2021.
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “Robust FD&I Methodology for Solenoid Pumps based on Discriminative Features,” presented at the Eastern European Machine Learning Summer School (EEML), Poland, July 1-9, 2020.
U. E. Akpudo and H. Jang-Wook, “Intelligent Solenoid Pump Fault Detection based on MFCC Features, LLE and SVM”, presented at the Second International Conference on AI in information and Communication (ICAIIC 2020) Fukuoka Japan, hosted by KICS, IEEE Communications Society, and IEICE-CS, February 19-21, 2020
Suju Kim, U. E. Akpudo, and H. Jang-Wook, “A Cost-Aware DNN-Based FDI Technology for Solenoid Pumps,” in Electronics, 10, 2323, 2021.
