Optimum Gasket Material Selection for PEM Fuel Cells Using Finite Element Analysis
Unlike the conventional design of PEMFC which are metal-based, the elastomeric characteristics of rubber gaskets offer superior advantages: maintaining elasticity through high deformations and loading conditions, manufacturing cost efficiency, and zero-leakage sealing (as desired in PEMFC designs). These, in addition to Pyung Hwa Industry Co., Ltd.’s niche for producing durable high-quality seals/gaskets were the major motivation for the research.
Silicone Vinyl Methyl Silicone (VMQ), Alkyl Acrylate Copolymer (ACM), nitrile-butadiene rubber (NBR), Fluro-Elastomer (FKM), Ethylene Propylene Diene Terpolymer (EPDM), etc. are some of the common materials used for PEMFC gaskets. While each of these materials have unique (and shared) physical and chemical property advantages like high elastic properties, thermal resistance, and resistance to hydrocarbons and oils, we were posed with the following questions—
Which of the popularly available materials should be prioritized during manufacturing?
Which hyperelastic model(s) should be prioritized for FEA-assisted material selection?
How possible is it to design a decision-making paradigm that integrates both factors (based on compatibility) for improved model and material selection?
These research questions propelled an eight-month-long project with Pyung Hwa Industry Co., Ltd., Korea that involved unilateral tensile testing at Pyung Hwa, exhaustive FEA which I spearheaded in our lab, and further empirical analyses by myself to draw meaningful conclusions to guide business decisions at Pyung Hwa while also educating the team members. 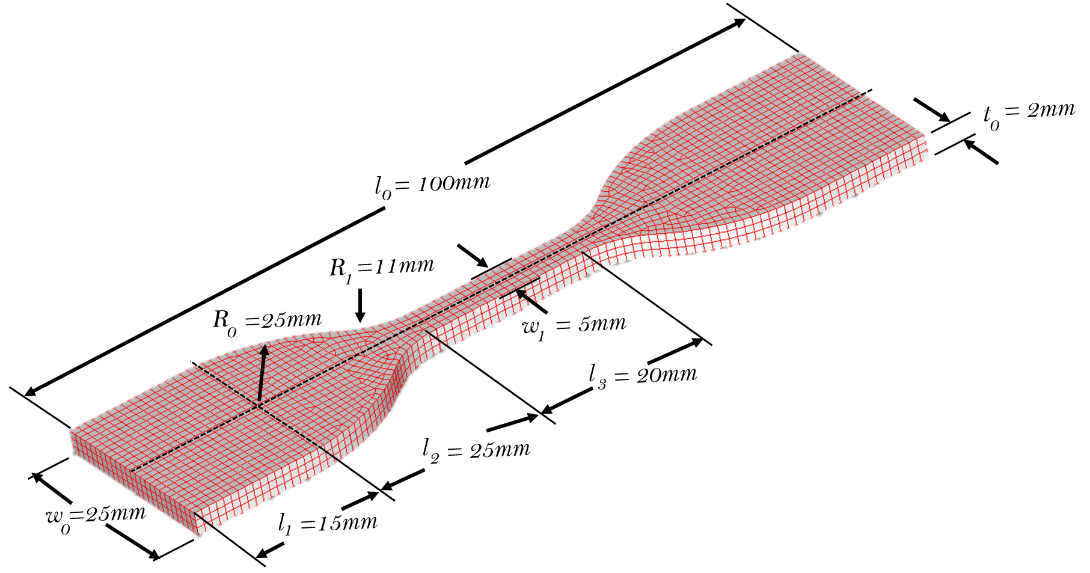
The major objectives of the project are:
- To conduct extensive reviews on PEMFC, rubber material properties, FEA, hyperelastic models, tensile testing, etc.
- Discovery of and validation of optimal material models (and parameters) between widely-recommended models using FEA-assisted evaluations and tensile testing results.
- To conduct uniaxial non-destructive tensile testing on different gaskets and digitally collect the stress and strain data
- To harness the stress and strain data for FEA using different hyperelastic models. This would help to discover their respective Young’s modulus and for further empirical analyses.
- Proposal of a reliable (and comprehensive) evaluation paradigm for the choice of (and validation) of material model
- To provide a data-driven paradigm for informed material selection and decision-making.
- To support continued research-based education in the related domains.
Our findings helped us draw valid conclusions/recommendations for Pyng Hwa towards improving their gasket production for commercial use.
Grants
- Grand Information Technology Research support (IITP-2020-2020-0-01612) provided by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT) South Korea (2020 -2021)
- Korean National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (No. NRF-2019R1I1A3A01063935) provided by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT) South Korea (2019).
- Agency for Defense Development grant (UD180018AD) provided by the RAM Specialized Laboratory, South Korea (2019).
Journal Publication from the project
- Kang-Min Cheon, U. E. Akpudo, Akeem Bayo Kareem, Okwuosa Chibuzo Nwabufo, and H. Jang-Wook, “An FEA-Assisted Decision-Making Framework for PEMFC Gasket Material Selection,” Energies, MDPI, vol. 15(7), pages 1-18, April.
