Rolling Element Bearing Failure Prognostics and RUL Estimation
Using a run-to-failure (R2F) experiment on four Rexnord ZA-2115 Rrolling element bearings conducted by The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), USA, this project develops a methodology for enhancing rolling element bearing (REB) prognostics by constructing a robust health indicator (HI) through the fusion of multiple highly monotonic statistical features derived from vibration monitoring data. 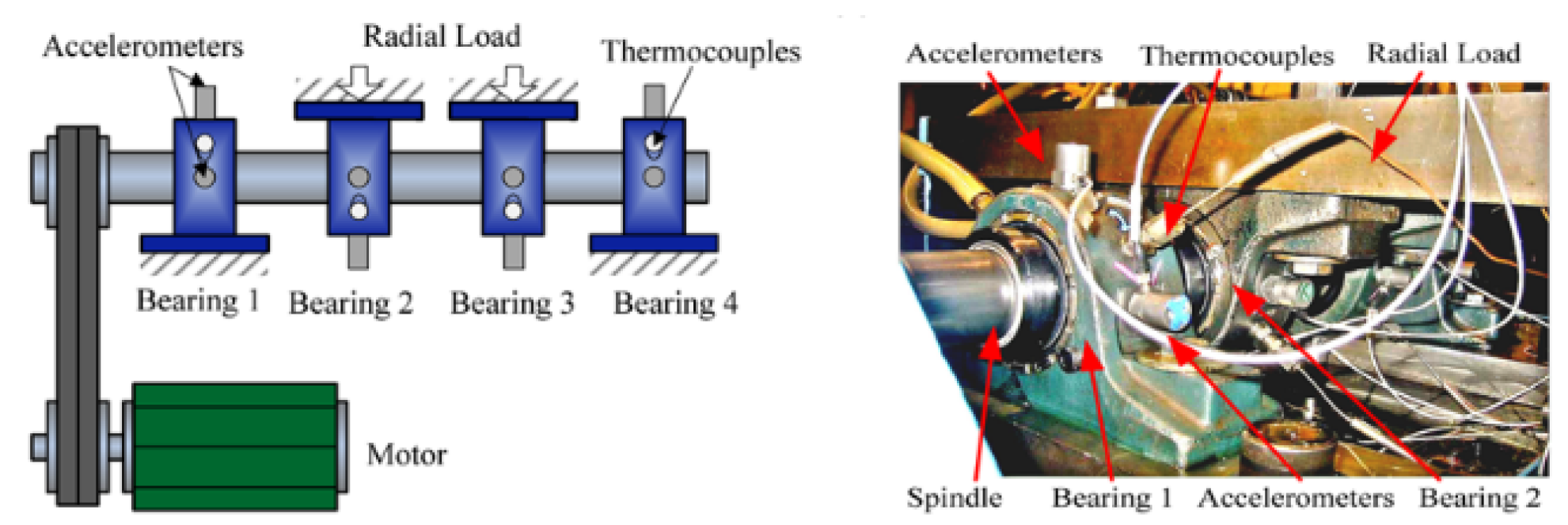
By integrating these features, the framework maps various degradation states and determines the optimal time-to-start prediction (TSP) through clustering algorithms that associate known failure modes with degradation clusters. A significant component of the study is the comparative analysis of predictive models for bearing degradation. It contrasts Bayesian machine learning with deep learning techniques. This comparison addresses critical considerations such as dependency, efficiency, and limitations of each approach.
Grants
- Korean National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant (No. NRF-2019R1I1A3A01063935) provided by the MSIT (Ministry of Science and ICT) South Korea (2019).
- Agency for Defense Development grant (UD180018AD) provided by the RAM Specialized Laboratory, South Korea (2019).
Journal PublicationS from the project
Akpudo, U., & Hur, J. W. (2020). A deep learning approach to prognostics of rolling element bearings. International Journal of Integrated Engineering, 12(3), 178-186.
Akpudo, U. E., & Hur, J. W. (2020). A deep learning approach to prognostics of rolling element bearings. International Journal of Integrated Engineering, 12(3), 178-186.
Akpudo, U. E., & Hur, J. W. (2020). A feature fusion-based prognostics approach for rolling element bearings. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology, 34, 4025-4035.
